Avert your eyes! My Sunday morning look at incompetency, corruption and policy failures:
• Trump’s Year of Anarchy: The Unconstrained Presidency and the End of American Primacy. (Foreign Affairs)
• The Crypto CEO Who’s Become Enemy No. 1 on Wall Street: Coinbase chief Brian Armstrong is clashing with Jamie Dimon and other bank stewards over the future of finance. (Wall Street Journal)
• Injury to Buildings and Vegetables: The ability to impose pollution on others is another aspect of class rule. (N+1)
• US Has Investigated Claims That WhatsApp Chats Aren’t Private: US law enforcement has been investigating allegations by former Meta Platforms Inc. contractors that Meta personnel can access WhatsApp messages, despite the company’s statements that the chat service is private and encrypted, according to interviews and an agent’s report seen by Bloomberg News. (Bloomberg)
• Trapped in the hell of social comparison: A hypothesis about why Americans are unhappy with their economy. (Noahpinion)
• On the architecture of unreality: Bari Weiss is not a journalist. She is a propagandist with a journalist’s title. She has an agenda. She has interests. And they align with the interests of those who think keeping the current regime in charge of our national affairs is theirs. It is why she brings the reactionary fraud Niall Ferguson to CBS: to lend the appearance of intellectual heft to what is, in fact, a project of epistemological sabotage. (Notes from the Circus) see also The commenters won: We are ruled, as it turned out, not only by ghouls, fascists, sociopaths, salesmen, influencers, mediocrities, and abusers, but by something stranger and potentially worse: Gawker commenters. Which Trump administration official is a former Gawker commenter? (Read Max)
• The Height of Close-Combat Weaponry Is on This Woman’s Doorstep: In pursuit of illegal immigrants, federal agents are carrying the instruments of war, fine-tuned and perfected for killing at short range. (New York Times)
• The Sins on the River Road Cannot Be Erased: How did a tiny industrial hub in Louisiana find itself at the center of America’s culture war? For St. John the Baptist Parish, the history is much deeper—and the costs of one age are stacked on the costs of another. (The Ringer)
• Police Who Once Backed ICE’s Mission Are Losing Faith in Its Tactics: In Minnesota and places where agents are deployed en masse, law-enforcement leaders are challenging whether they are adhering to the stated mission. ICE says operations are lawful and targeted. (Wall Street Journal) see also Police and ICE Agents Are on a Collision Course: After another fatal ICE shooting in Minneapolis, the rift between local police and federal agents is becoming a rupture. (The Atlantic)
• Forgotten Star Dorothy Stratten Almost Lived the Hollywood Fairy Tale. It Ended as a Horror Story. Peter Bogdanovich, Bob Fosse, and Hugh Hefner all loved her, in their own ways—for better and worse. This reexamination of Stratten’s life, rape, and murder casts a new light on the angel who was a centerfold. (Vanity Fair)
Be sure to check out our Masters in Business interview this weekend with Kate Burke, CEO of Allspring Global Investments a global asset manager with more than 600 billion dollars in assets under advisement. She is also a director on the firm’s board. Previously, she was at AllianceBernstein as COO/CFO.
Average 50-something American is worth $1.4 million; Average 20-something $127,730
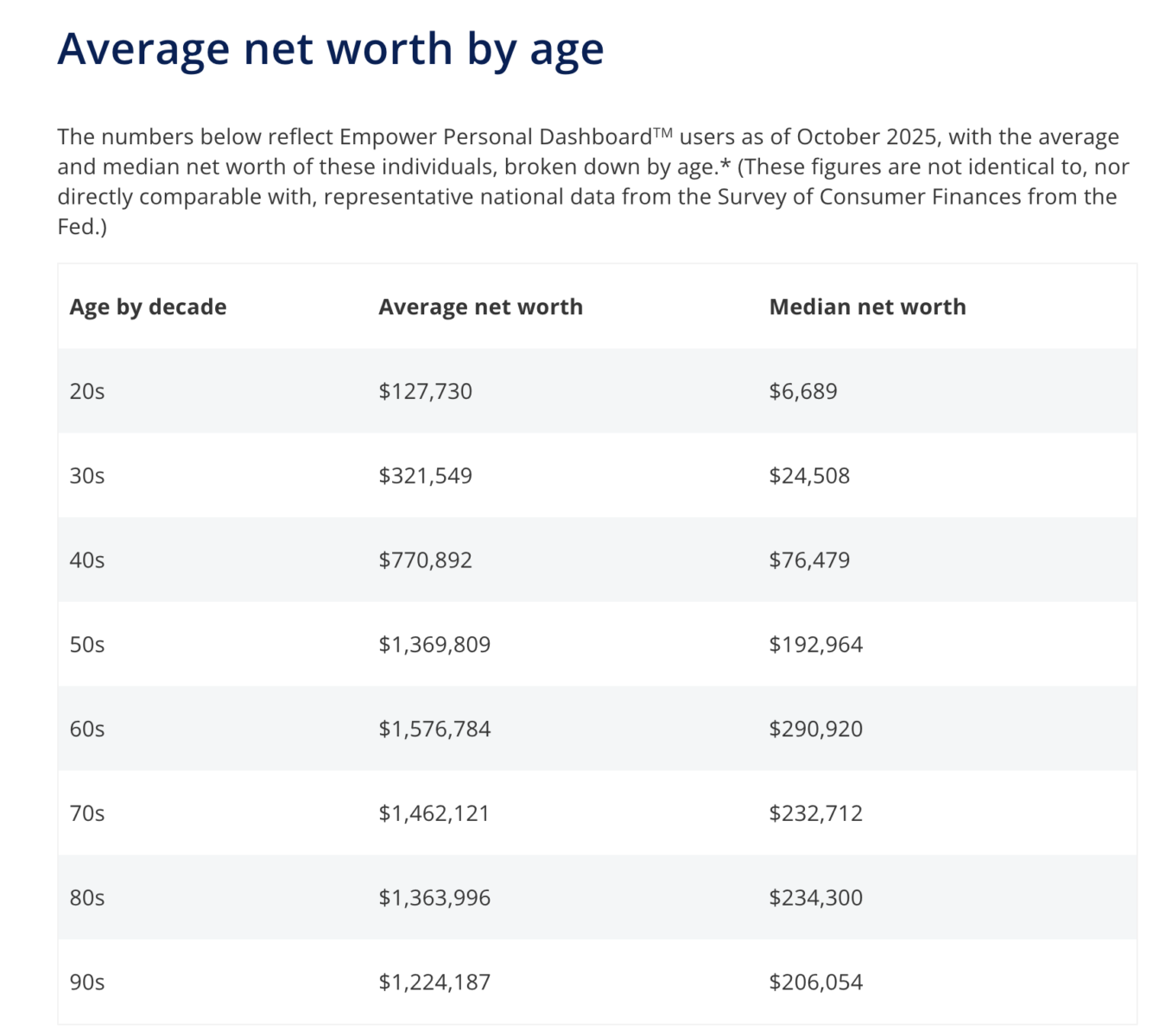
Source: Empower
Sign up for our reads-only mailing list here.
~~~
To learn how these reads are assembled each day, please see this.
The post 10 Sunday Morning Reads appeared first on The Big Picture.
Peter Schiff: Printing Money Is Not the Cure for Cononavirus
In his most recent podcast, Peter Schiff talked about coronavirus and the impact that it is having on the markets.
Earlier this month, Peter said he thought the virus was just an excuse for stock market woes. At the time he believed the market was poised to fall anyway. But as it turns out, coronavirus has actually helped the US stock market because it has led central banks to pump even more liquidity into the world financial system.
All this means more liquidity — central banks easing. In fact, that is exactly what has already happened, except the new easing is taking place, for now, outside the United States, particularly in China.”
Although the new money is primarily being created in China, it is flowing into dollars — the dollar index is up — and into US stocks. Last week, US stock markets once again made all-time record highs.
In fact, I think but for the coronavirus, the US stock market would still be selling off. But because of the central bank stimulus that has been the result of fears over the coronavirus, that actually benefitted not only the US dollar, but the US stock market.”
In the midst of all this, Peter raises a really good question.
The primary economic concern is that coronavirus will slow down output and ultimately stunt economic growth. Practically speaking, the world would produce less stuff. If the virus continues to spread, there would be fewer goods and services produced in a market that is hunkered down.
Why would the Federal Reserve respond, or why would any central bank respond to that by printing money? How does printing more money solve that problem? It doesn’t. In fact, it actually exacerbates it. But you know, everybody looks at central bankers as if they’ve got the solution to every problem. They don’t. They don’t have the magic wand. They just have a printing press. And all that creates is inflation.”
Sometimes the illusion inflation creates can look like a magic wand. Printing money can paper over problems. But none of this is going to fundamentally fix the economy.
In fact, if central bankers were really going to do the right thing, the appropriate response would be to drain liquidity from the markets, not supply even more.”
Peter explained how the Fed was originally intended to create an “elastic” money supply that would expand or contract along with economic output. Today, the money supply only goes in one direction — that’s up.
The economy is strong, print money. The economy is weak, print even more money.”
Of course, the asset that’s doing the best right now is gold. The yellow metal pushed above $1,600 yesterday. Gold is up 5.5% on the year in dollar terms and has set record highs in other currencies.
Because gold is rising even in an environment where the dollar is strengthening against other fiat currencies, that shows you that there is an underlying weakness in the dollar that is right now not being reflected in the Forex markets, but is being reflected in the gold markets. Because after all, why are people buying gold more aggressively than they’re buying dollars or more aggressively than they’re buying US Treasuries? Because they know that things are not as good for the dollar or the US economy as everybody likes to believe. So, more people are seeking out refuge in a better safe-haven and that is gold.”
Peter also talked about the debate between Trump and Obama over who gets credit for the booming economy – which of course, is not booming.
We are living in crazy times. I have a hard time believing that most of the general public is not awake, but in reality, they are.
We've never seen anything like this; I mean not even under Obama during the worst part of the Great Recession."
Now the Fed is desperately trying to keep interest rates from rising. The problem is that it's a much bigger debt bubble this time around , and the Fed is going to have to blow a lot more air into it to keep it inflated.
The difference is this time it's not going to work."
It looks like the Fed did another $104.15 billion of Not Q.E. in a single day. The Fed claims it's only temporary. But that is precisely what Bernanke claimed when the Fed started QE1. Milton Freedman once said, "Nothing is so permanent as a temporary government program." The same applies to Q.E., or whatever the Fed wants to pretend it's doing. Except this is not QE4, according to Powell. Right. Pumping so much money out, and they are accusing China of currency manipulation ? Wow! Seriously! Amazing!
Dump the U.S. dollar while you still have a chance.
Welcome to The Atlantis Report.
And it is even worse than that, In addition to the $104.15 billion of "Not Q.E." this past Thursday; the FED added another $56.65 billion in liquidity to financial markets the next day on Friday.
That's $160.8 billion in two days!!!! in just 48 hours.
That is more than 2 TIMES the highest amount the FED has ever injected on a monthly basis under a Q.E. program (which was $80 billion per month)
Since this isn't QE....it will be really scary on what they are going to call Q.E. Will it twice, three times, four times, five times what this injection per month
! It is going to be explosive since it takes about 60 to 90 days for prices to react to this, January should see significant inflation as prices soak up the excess liquidity. The question is, where will the inflation occur first
. The spike in the repo rate might have a technical explanation: a misjudgment was made in the Fed's money market operations. Even so, two conclusions can be drawn: managing the money markets is becoming harder, and from now on, banks will be studying each other's creditworthiness to a greater degree than before.
Those people, who struggle with the minutiae of money markets, and that includes most professionals, should focus on the causes and not the symptoms. Financial markets have recovered from each downturn since 1980 because interest rates have been cut to new lows. Post-2008, they were cut to near zero or below zero in all major economies. In response to a new financial crisis, they cannot go any lower. Central banks will look for new ways to replicate or broaden Q.E. (At some point, governments will simply see repression as an easier option).
Then there is the problem of 'risk-free' assets becoming risky assets. Financial markets assume that the probability of major governments such as the U.S. or U.K. defaulting is zero. These governments are entering the next downturn with debt roughly twice the levels proportionate to GDP that was seen in 2008.
The belief that the policy worked was completely predicated on the fact that it was temporary and that it was reversible, that the Fed was going to be able to normalize interest rates and shrink its balance sheet back down to pre-crisis levels. Well, when the balance sheet is five-trillion, six-trillion, seven-trillion when we're back at zero, when we're back in a recession, nobody is going to believe it is temporary. Nobody is going to believe that the Fed has this under control, that they can reverse this policy. And the dollar is going to crash. And when the dollar crashes, it's going to take the bond market with it, and we're going to have stagflation. We're going to have a deep recession with rising interest rates, and this whole thing is going to come imploding down.
everything is temporary with the fed including remaining off the gold standard temporary in the Fed's eyes could mean at least 50 years
This liquidity problem is a signal that trading desks are loaded up on inventory and can't get rid of it. Repo is done out of a need for cash. If you own all of your securities (i.e., a long-only, no leverage mutual fund) you have no need to "repo" your securities - you're earning interest every night so why would you want to 'repo' your securities where you are paying interest for that overnight loan (securities lending is another animal). So, it is those that 'lever-up' and need the cash for settlement purposes on securities they've bought with borrowed money that needs to utilize the repo desk.
With this in mind, as we continue to see this need to obtain cash (again, needed to settle other securities purchases), it shows these firms don't have the capital to add more inventory to, what appears to be, a bloated inventory. Now comes the fun part: the Treasury is about to auction 3's, 10's, and 30-year bonds. If I am correct (again, I could be wrong), the Fed realizes securities firms don't have the shelf space to take down a good portion of these auctions. If there isn't enough retail/institutional demand, it will lead to not only a crappy sale but major concerns to the street that there is now no backstop, at all, to any sell-off. At which point, everyone will want to be the first one through the door and sell immediately, but to whom?
If there isn't enough liquidity in the repo market to finance their positions, the firms would be unable to increase their inventory. We all saw repo shut down on the 2008 crisis. Wall St runs on money. . OVERNIGHT money. They lever up to inventory securities for trading. If they can't get overnight money, they can't purchase securities. And if they can't unload what they have, it means the buy-side isn't taking on more either.
Accounts settle overnight. This includes things like payrolls and bill pay settlements.
If a bank doesn't have enough cash to payout what its customers need to pay out, it borrows. At least one and probably more than one banks are insolvent. That's what's going on.
First, it can't be one or two banks that are short. They'd simply call around until they found someone to lend. But they did that, and even at markedly elevated rates, still, NO ONE would lend them the money. That tells me that it's not a problem of a couple of borrowers, it's a problem of no lenders. And that means that there's no bank in the world left with any real liquidity. They are ALL maxed out.
But as bad as that is, and that alone could be catastrophic, what it really signals is even worse. The lending rates are just the flip side of the coin of the value of the assets lent against. If the rates go up, the value goes down. And with rates spiking to 10%, how far does the value fall? Enormously! And if banks had to actually mark down the value of the assets to reflect 10% interest rates, then my god, every bank in the world is insolvent overnight. Everyone's capital ratios are in the toilet, and they'd have to liquidate. We're talking about the simultaneous insolvency of every bank on the planet. Bank runs. No money in ATMs, Branches closed. Safe deposit boxes confiscated. The whole nine yards, It's actually here. The scenario has tended to guide toward for years and years is actually happening RIGHT NOW! And people are still trying to say it's under control. Every bank in the world is currently insolvent. The only thing keeping it going is printing billions of dollars every day. Financial Armageddon isn't some far off future risk. It's here. Prepare accordingly.
This fiat system has reached the end of the line, and it's not correct that fiat currencies fail by design. The problem is corruption and manipulation. It is corruption and cheating that erodes trust and faith until the entire system becomes a gigantic fraud. Banks and governments everywhere ARE the problem and simply have to be removed. They have lost all trust and respect, and all they have left is war and mayhem. As long as we continue to have a majority of braindead asleep imbeciles following orders from these psychopaths, nothing will change.
Fiat currency is not just thievery. Fiat currency is SLAVERY.
Ultimately the most harmful effect of using debt of undefined value as money (i.e., fiat currencies) is the de facto legalization of a caste system based on voluntary slavery.
The bankers have a charter, or the legal *right*, to create money out of nothing.
You, you don't. Therefore you and the bankers do not have the same standing before the law. The law of the land says that you will go to jail if you do the same thing (creating money out of thin air) that the banker does in full legality.
You and the banker are not equal before the law. ALL the countries of the world; Islamic or secular, Jewish or Arab, democracy or dictatorship; all of them place the bankers ABOVE you.
And all of you accept that only whining about fiat money going down in exchange value over time (price inflation which is not the same as monetary inflation). Actually, price inflation itself is mainly due to the greed and stupidity of the bankers who could keep fiat money's exchange value reasonably stable, only if they wanted to.
Witness the crash of silver and gold prices which the bankers of the world; Russian, American, Chinese, Jewish, Indian, Arab, all of them collaborated to engineer through the suppression and stagnation of precious metals' prices to levels around the metals' production costs, or what it costs to dig gold and silver out of the ground.
The bankers of the world could also collaborate to keep nominal prices steady (as they do in the case of the suppression of precious metals prices). After all, the ability to create fiat money and force its usage is a far more excellent source of power and wealth than that which is afforded simply by stealing it through inflation. The bankers' greed and stupidity blind them to this fact. They want it all, and they want it now.
In conclusion,
The bankers can create money out of nothing and buy your goods and services with this worthless fiat money, effectively for free. You, you can't.
You, you have to lead miserable existences for the most of you and WORK in order to obtain that effectively nonexistent, worthless credit money (whose purchasing/exchange value is not even DEFINED thus rendering all contracts based on the null and void!) that the banker effortlessly creates out of thin air with a few strokes of the computer keyboard, and which he doesn't even bother to print on paper anymore, electing to keep it in its pure quantum uncertain form instead, as electrons whizzing about inside computer chips which will become mute and turn silent refusing to tell you how many fiat dollars or euros there are in which account, in the absence of electricity. No electricity, no fiat, nor crypto money.
It would appear that trust is deteriorating as it did when Lehman blew up .
Something really big happened that set off this chain reaction in the repo markets. Whatever that something is, we aren't be informed. They're trying to cover it up, paper it over with conjured cash injections, play it cool in front of the cameras while sweating profusely under the 5 thousands dollar suits. I'm guessing that the final high-speed plunge into global economic collapse has begun. All we see here is the ripples and whitewater churning the surface, but beneath the surface, there is an enormous beast thrashing desperately in its death throws. Now is probably the time to start tying up loose ends with the long-running prep projects, just saying. In other words, prepare accordingly, and
Get your money out of the banks. I don't care if you don't believe me about Bitcoin. Get your money out of the banks. Don't keep any more money in a bank than you need to pay your bills and can afford to lose.
The Financial Armageddon Economic Collapse Blog tracks trends and forecasts , futurists , visionaries , free investigative journalists , researchers , Whistelblowers , truthers and many more
The Financial Armageddon Economic Collapse Blog tracks trends and forecasts , futurists , visionaries , free investigative journalists , researchers , Whistelblowers , truthers and many more


Recent comments