February Snapshot Of The Global Nuclear Industry
While February saw continued volatility with uranium spot prices after they pulled back from barely breaking into the triple digit range in January, the other metric that remains flat as a board is the number of reactors currently under construction in the U.S. which stands at a solid zero. Reflected against the backdrop of China, as they added one additional reactor for a total of 39 under construction, the frustration for actually launching a nuclear renaissance intensifies for everyone.
TerraPower did recently receive their construction permit for deploying a Natrium reactor in Wyoming, but it will potentially take months for them to meet the actual requirement of getting added to the board. The U.S. should look forward to joining the prestigious ranks alongside Iran for having just one reactor under construction.
Just as we stated in our uranium investment thesis published back in December of 2020 and even more recently in December of last year, we expect uranium to remain a solid choice for the nuclear renaissance.
Goldman Sachs analyst Brian Lee provides a recap for the month of February regarding updates across the uranium and nuclear industries.
New reactor progress and announcements
North America
2/13/2026 - Canada - OPG and Port Hope are collaborating to develop up to 10GW of nuclear capacity at the Wesleyville site, potentially powering 10 million homes. The project includes C$5mn in community funding to support regulatory assessments and local job creation.
2/19/2026 - Canada - Bruce Power has completed the construction phase of the Unit 3 Major Component Replacement, replacing key reactor parts to extend its operating life by up to 35 years. With regulatory approval to begin fuel loading, the unit is on track to return to Ontario’s grid ahead of schedule and on budget.
2/20/2026 - United States - Governor of Illinois, JB Pritzker, has issued an executive order to accelerate the deployment of at least 2GW of new nuclear capacity by 2033. This initiative follows the lifting of a long-standing moratorium and aims to support the state’s goal of 100% carbon-free energy by mid-century.
2/27/2026 - United States - Vistra Corp has secured landmark 20-year PPA with Amazon Web Services and Meta to provide over 3,800 MW of nuclear energy, supporting the long-term relicensing and uprating of its plants through the 2050s and 2060s. While initial power delivery is set to begin in 2026, the planned capacity uprates at the Perry, Davis-Besse, and Beaver Valley facilities are expected to come online between 2031 and 2034.
Europe
2/5/26 - Hungary - Hungary has officially commenced construction of the Paks II nuclear power plant with the first concrete pour for the foundation of Unit 5. The project, featuring two Russian VVER-1200 reactors, aims to provide approximately 70% of the nation’s electricity demand by the early 2030s.
2/10/2026 - Armenia - Armenia and the United States have finalized a “123 Agreement” for nuclear cooperation, enabling up to $9bn in potential US exports and long-term support for projects such as SMRs. This agreement establishes a framework for American technology to compete with Russian and international offers as Armenia prepares to select a new reactor model by 2026 or 2027.
2/13/2026 - France - France’s latest Multiannual Energy Programme for 2026–2035 puts nuclear at the centre of decarbonisation—seeking to extend existing reactors’ lifetimes, build six new reactors (with an option to decide on eight more), and raise decarbonised electricity output while cutting fossil fuel consumption, alongside renewables.
2/18/2026 - Slovenia - Slovenia has officially initiated the National Spatial Plan for a new reactor unit at the Krško Nuclear Power Plant. Prime Minister Robert Golob announced that a referendum is expected by late 2027 or early 2028, at which point the technology, supplier, and final costs will be defined.
2/23/2026 - Serbia - Serbia and Russia have discussed expanding nuclear energy cooperation, with Rosatom offering a full range of technologies from SMRs to large-scale plants to support Serbia’s energy sovereignty. While Serbia is currently working with France’s EDF on its initial nuclear roadmap, the government aims to establish a national implementation organization by the end of March 2026 to prepare for potential grid connection after 2040.
Asia and other
2/3/2026 - Kazakhstan - Kazakhstan has finalized the selection of the Zhambyl district in the Almaty region for its second nuclear power plant, with the China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC) appointed to lead the construction. This project, alongside the first plant to be built by a Rosatom-led consortium, is part of a strategic plan to diversify the national energy mix and achieve a 5% nuclear power generation share by 2035.
2/9/2026 - Japan - Tepco has restarted Unit 6 of the Kashiwazaki-Kariwa nuclear power plant, marking the first time a reactor owned by the company has operated since the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi accident. The 1,356 MWe ABWR reached criticality on February 17,2026, and is scheduled to return to commercial operation by March 18,2026.
2/11/2026 - India - India’s indigenous 700 MWe Rajasthan Unit 7 has successfully reached its full operating capacity following its initial grid synchronization. This milestone represents a significant step forward in expanding India’s domestic nuclear power generation and clean energy infrastructure.
2/16/2026 - China - Unit 1 of the San’ao nuclear power plant in Zhejiang, China, reached first criticality on 2/14. This Hualong One reactor is the first of 6 units planned for the site and marks the first instance of private capital investment in a Chinese nuclear project.
2/16/2026 - China - Unit 1 of the Taipingling nuclear power plant has successfully connected to the grid, marking the first of six planned Hualong One reactors to supply electricity in Guangdong province. This 1116 MWe reactor is expected to enter commercial operation in the first half of 2026.
2/16/2026 - India - Tarapur Atomic Power Station Unit-1 (TAPS−1), India’s oldest commercial nuclear reactor, has returned to service following an extensive refurbishment and life-extension program. The 160MWe boiling water reactor reached criticality on December 30,2025, and has now been synchronized to the grid with upgraded safety systems and modernized equipment.
2/19/2026 - Russia - Rostekhnadzor has issued a 10-year operating license for Unit 2 of the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant, signaling Russia’s intent to bring the facility under its regulatory framework for future power generation. While all six units remain shut down, Rosatom continues to seek licenses for the remaining reactors, including an active application for Unit 6 and plans for the rest by the end of 2026.
3/2/2026 - India - India has officially started construction on Kaiga units 5 and 6 following the first pour of concrete for the two 700 MMe indigenous reactors. This $1.5bn project uses an innovative “mega EPC” strategy to support India’s goal of reaching 100 GW of nuclear capacity by 2047.
3/4/2026 - Turkiye - Candu Energy and Türkiye Nuclear Energy Company signed an MoU to assess deploying Canadian CANDU reactors in Turkiye, covering technical data exchange, site suitability, and regulatory/licensing needs. The review also examines financing and delivery models, localisation, and workforce development as Turkiye expands its nuclear programme beyond Akkuyu.
3/4/2026 - Philippines - KHNP, Korea Eximbank, and Manila Electric Company signed an MoU to support nuclear power plant development in the Philippines, including feasibility work, site selection, and workforce training. Korea Eximbank will also explore financing packages to help fund projects and support participating Korean firms.
SMR announcement tracker
2/12/2026 - Norway - Norway’s Ministry of Energy has officially established the impact assessment program for Norsk Kjernekraft’s proposed SMR plant in the Taftøy industrial park. This regulatory milestone enables the formal evaluation of environmental and safety factors for the project, which aims to generate ~12.5 TWh of electricity annually.
2/13/2026 - Romania - Nuclearelectrica’s shareholders have approved the FID for Romania’s first SMR plant in Doicești, which will utilize NuScale technology to provide 462 MWe of clean capacity by 2033. The project, estimated to cost between $6bn-$7bn, is now transitioning into a financial structuring and pre-engineering phase to secure investors and finalize supply chain logistics. See our report on the news.
2/17/2026 - Philippines - The USTDA has announced $2.7mn in funding for Meralco PowerGen Corp to evaluate American SMR designs and develop an implementation roadmap for the Philippines’ first nuclear plant. This initiative, supported by the bilateral “123 Agreement,” aims to enhance energy security and establish a qualified nuclear workforce through technical assistance, simulators, and university partnerships.
2/17/2026 - Finland - Steady Energy has begun constructing a full-scale, non-nuclear pilot of its LDR-50 reactor in Helsinki to test operational features and establish supply chains for district heating. The $17mn to $23mn project uses an electric heat source to provide 6 MW of thermal output, paving the way for commercial 50 MW underground nuclear heating plants.
2/23/2026 - United States - Kairos Power and DOE’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory signed a $27mn, five‑year partnership to test and validate Kairos’s fluoride salt‑cooled, TRISO‑fueled reactor technology and support the Hermes demonstration program in Oak Ridge, Tennessee.
2/25/2026 - Poland - GE Vernova Hitachi and Orlen Synthos Green Energy (OSGE) have signed an agreement to develop a standardized technical design for the BWRX-300 SMR tailored to Polish regulations and safety standards. This generic design aims to accelerate the deployment of a planned fleet of 24 reactors across Poland, with the first unit in Włocławek targeted for completion by 2032.
2/25/2026 - UAE - NANO Nuclear Energy and EHC Investment LLC have signed an MoU to explore deploying KRONOS MMRs for industrial and data center use in the UAE. These transportable, 15 MWe reactors provide a water-free, scalable clean energy solution to support the region’s decarbonization and energy resilience goals.
2/27/2026 - Lithuania - Lithuania’s Altra and GE Vernova Hitachi have signed an MoU to evaluate the feasibility of deploying BWRX-300 SMRs to meet the country’s projected energy needs. This assessment supports Lithuania’s goal of reaching climate neutrality by 2050, with a formal decision on SMR installation expected by 2028.
3/3/2026 - Singapore - KHNP and Singapore’s Energy Market Authority (EMA) have signed an MoU to jointly study the feasibility of SMRs for Singapore. This collaboration focuses on technical information sharing and human resource development to support Singapore’s long-term decarbonization and energy security goals.
Global reactor critical updates
In the month of February, there have been few changes to new reactor construction
starts, grid connections, shutdowns, or restarts.

Global reactor construction tracker

Global reactors under construction

China only

Fuel announcements
2/6/2026 - United States - BWXT is finalizing TRISO fuel for Antares Nuclear’s pilot reactor, targeting criticality by July 4, 2026, under a DOE acceleration initiative. The Antares R1 is a transportable, sodium heat pipe-cooled microreactor designed to provide up to 1MWe of scalable, carbon-free power.
2/11/2026 - United States - Solstice Advanced Materials is pursuing an expansion to boost UF6 output at its Metropolis Works plant to over 10,000 tonnes in 2026. The company says debottlenecking and further capacity projects are supported by strong demand and a backlog of more than $2bn.
2/13/2026 - Namibia - Bannerman Energy struck a financing and JV deal with CNNC Overseas for Namibia’s Etango uranium project: Bannerman will hold 55% and CNOL 45% of a JV that owns 95% of Etango, with CNOL investing about $294.5mn (plus up to $27mn reimbursement) and receiving 60% life-of-mine offtake, aiming to enable debt-free construction subject to approvals.
2/16/2026 - United States -The U.S. NRC issued TRISO-X a 40-year special nuclear material licence under 10 CFR Part 70 to commercially fabricate TRISO fuel using HALEU at its Tennessee facilities (TX-1 and TX-2), with operations starting after a final NRC pre-startup inspection. TX-1 is expected to produce about 5 tonnes of uranium (about 700,000 TRISO pebbles) per year.
2/17/2026 - Kazakhstan - Kazatomprom said its 2025 uranium output rose about 10–11% yoy to 67.18mn/lb U3O8 (100% basis), mainly from ramp-up at JV Budenovskoye, and guided 2026 production at 27,500–29,000 tU (100% basis), subject to sulphuric acid availability and consistent with its value-over-volume strategy. For more details on CCJ, please see our earnings takeaways note.
2/20/2026 - Denmark - Copenhagen Atomics signed a non-binding Letter of Intent with Rare Earths Norway to secure future access to thorium from Norway’s Fensfeltet deposit to support its containerised molten salt reactor plans, with a first test reactor expected at the Paul Scherrer Institute and commercial deployment targeted in the early 2030s.
2/24/2026 - United States - Orano submitted an Environmental Report for Project IKE to the NRC, moving the project into the next NRC review phase; Orano noted the licensing process can take up to three years, and low-enriched uranium production is scheduled to begin in 2031.
2/24/2026 - Brazil - INB, ENBPar, and Galvani met Ceará’s governor to align licensing and discuss infrastructure for the Santa Quitéria Project at Fazenda Itataia, targeting about 2,300t/year of uranium concentrate for Angra 1, Angra 2, and future Angra 3; it remains in preliminary environmental licensing with IBAMA, accepted for review in March 2022.
2/25/2026 - Russia - Rosatom says its uranium miners hit 2025 production targets and are expanding their resource base, including new licences and added infrastructure to support new deposits. It also highlighted a Krasnokamensk power-plant modernisation to support mining operations and noted growing non-uranium revenue alongside these plans.
2/25/2026 - Canada - Denison Mines says its Board approved building the Phoenix ISR uranium project at Wheeler River in Saskatchewan, with site prep and construction starting next month and first production targeted for mid-2028. The company says Phoenix could be Canada’s first ISR uranium mine.
2/25/2026 - United States - Deep Fission says it has signed a supply agreement to buy LEU from Urenco USA’s enrichment plant in Eunice, New Mexico, to support testing of its 15MWe underground Gravity SMR and early commercial deployment.
3/2/2026 - India - Cameco will supply India’s Department of Atomic Energy nearly 22mn lbs of U3O8 from 2027–2035 on market-linked pricing, a deal estimated at about C$2.6bn, as India ramps up nuclear capacity and other suppliers (e.g., Kazatomprom) also pursue long-term sales; the contract adds to India’s efforts to secure reliable uranium supply for its planned reactor expansion. Please see our note on the deal.
Uranium pricing and volume trackers
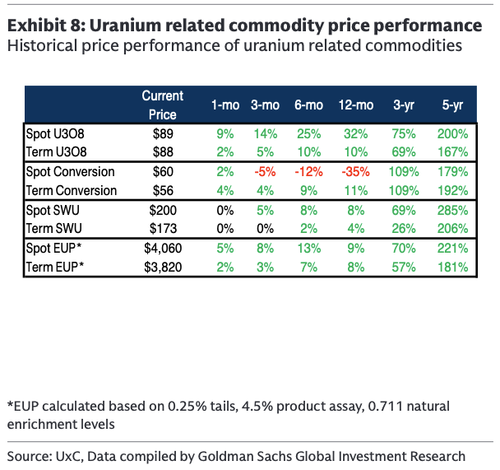
Spot pricing volatile. After a strong start to the year, spot pricing was on a downward trajectory throughout almost all of February. Specifically, spot pricing dropped from ~$94/lb to ~$85/lb in the first week of February, with a slight uptick in the following week with prices climbing back up to ~$90/lb, then followed by a modest decline ever since and currently settling at ~$86/lb. Spot market activity was moderate in the month with a total of 47 transactions involving ~6mn/lbs of uranium, with SPUT being relatively less active this month when compared to the last. Compared to last year, 2026 has started stronger in terms of spot activity.
Term pricing uptick. Term pricing for uranium continued its upward momentum from January, increasing another $2 to reach $90/lb, a level not seen since May 2008. Term market activity remained moderate throughout February, with a total of four utility term contract awards reported: three for uranium (U3O8) and one for conversion services. Additionally, some non-utility mid-term uranium purchases were tracked. Several utilities were actively evaluating offers, including one for nearly 1.2mn/lb of uranium with deliveries starting in 2029, and non-U.S. utilities assessing longer-term requests for uranium and EUP with deliveries extending into the mid-2030s. Offer levels indicated continued upward pressure on term prices, with floor pricing reaching the mid-$70s and ceiling prices pushing into the $125-$130 range, with some even reaching the mid-$150s.
Tyler Durden
Wed, 03/11/2026 - 19:45
 via India Today
via India Today



 Blocks with symbols and atomic numbers of Rare Earth Elements (REE) are placed on a Chinese flag in this illustration taken January 21, 2026. REUTERS/Dado Ruvic/Illustration/File Photo
Blocks with symbols and atomic numbers of Rare Earth Elements (REE) are placed on a Chinese flag in this illustration taken January 21, 2026. REUTERS/Dado Ruvic/Illustration/File Photo
 LeBlanc prepares to hand a shotgun to a PhantomMattia Balsamini for TIME. Source: TIME
LeBlanc prepares to hand a shotgun to a PhantomMattia Balsamini for TIME. Source: TIME


 suwijaknook6644689/Shutterstock
suwijaknook6644689/Shutterstock





Recent comments